| KLD amp kits building primer |
If you are not familiar with the basics of electronics, please take some time to learn below about electronic components used in tube guitar amp and what are several parts consisted one amp. |
| 1.Understand constitution sections of amp circuit Before soldering, know what you're building and how it works. A tube guitar amp circuit is made up of: 1.1Rectifier: This can be either solid-state or vacuum tube. In both cases, the rectifier converts high-voltage AC into DC voltage. Tube rectifiers require a 5V or 6V filament winding from the power transformer to operate. 1.2 Power supply: This is important! Each amp has a power supply , which supplies power to different parts of the amp. It involves the power transformer, filter caps, rectifier and other components, depending on the amp. What the voltage is depends on the type of amp it is. Is it a cathode bias or fixed bias amp? Does it have 2,3, or 4 stages of filtering? Does it have a reverb driver? Etc. You'll need to know this information for ease of troubleshooting and keeping yourself safe. 1.3 Preamp section: This is where your signal is amplified and sent through various stages for further amplification and tone shaping using different potentiometers. 1.4Tone control : the section of the circuit that shapes the frequency response of your guitar signal essentially adjusting how much bass, mids, and treble are present in the output. It helps tailor the sound character, from warm and mellow to bright and cutting. More about Tone stack , please watch : How The Guitar Amp Tone Stack Work Phase Inverter: Some amps have them and some don’t. There are also different types of phase inverter circuits. It may be best to research phase inverters separately as this is a topic that encompasses a ton of information. 1.5 Output section: This is what does the heavy lifting for the amp. It takes the preamp signal and boosts it via the output transformer, tube plates, negative feedback loop, etc. 1.6 Bias circuits: This is what regulates the idle of the output tubes so the amp can run efficiently. This voltage is negative on fixed-bias amps. There are fixed-bias amps, cathode-biased amps and fixed-bias amps with a bias balance. Know what all three are and note the differences. |
2. The components used in amp. |
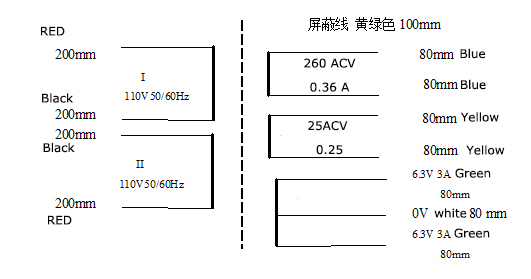 |
| For high-power amps such as the JCM25 or Bassman25, one 6.3V AC port can be used for the filaments of the preamp tubes (using 6.3V-0V), and the other 6.3V AC port for the filaments of the power tubes. For low-power amps such as the PVA18 or UT18, a single 6.3V AC port can be used to power the filaments of all tubes. |
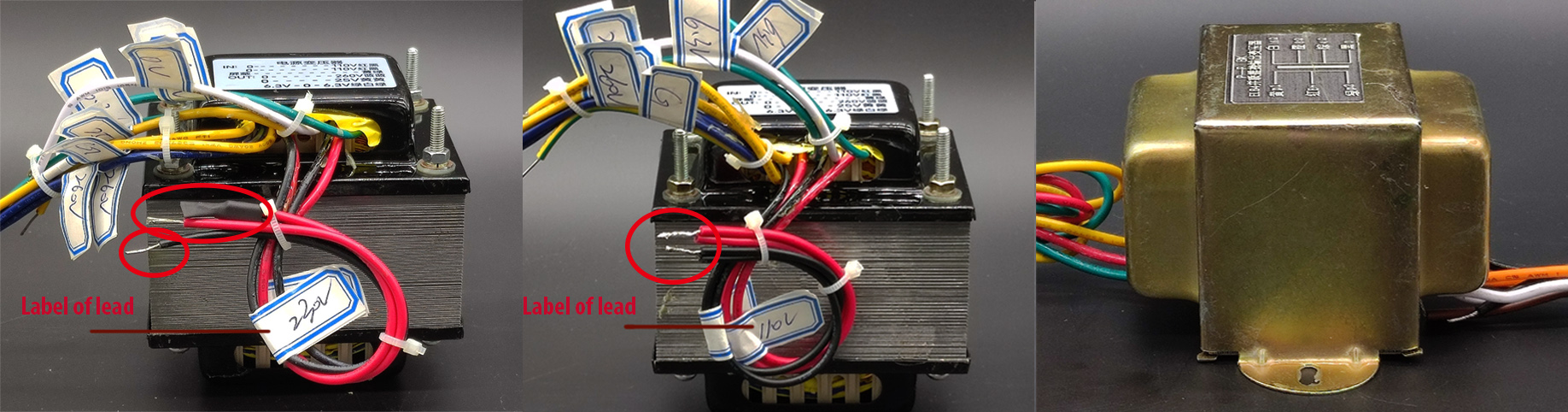 |
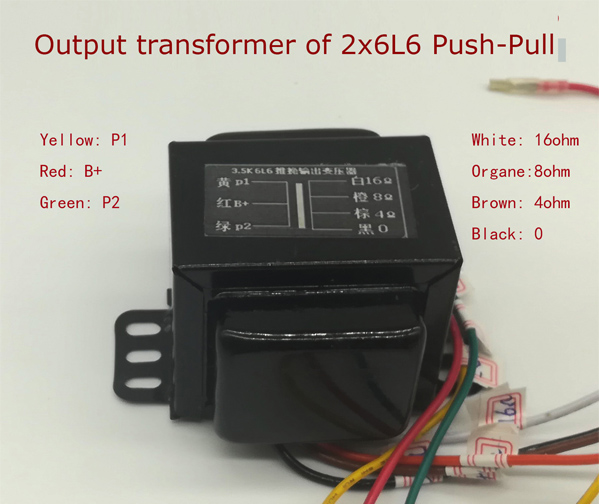
| 2.2 Output transformer: |
| Tips:REMEMBER: DO NOT OPERATE YOUR AMP WITHOUT A LOAD.CONFIRM LOAD CONNECTED, BEFORE YOU TURN ON AMP. |
|
(a)Primary coil: |
 |
| 2.3 Vacuum tube (a) Preamp vacuum tube: These are most commonly 9 pin (noval) tubes that can have 2 triodes in the same glass envelope. Examples are 12AY7, 12AT7, 12AX7, 7025, 5751, etc. (b) Output( power) vacuum tube: These are larger than preamp tubes and have various methods of operation. They are commonly 8 pin (octal) pentodes, power beam tubes, and tetrodes. These are limited to one amplification circuit per tube. Examples are 6V6, 6L6, EL34, EL84, KT88's etc. (c) Tube anatomy: Tubes can be called a diode, a triode, a pentode, or a tetrode, depending on the construction of the tube itself. Even though they may have the same base that fits your socket, this doesn't mean it will work. All tubes will have a cathode and a plate. This makes up a diode. When you add components like a control grid, screen and suppressor, the tube type changes. (d)Filament wiring: This is usually to Pins 2 and 7 on the octals and Pins 4+5 and 9(common pin)on Noval sockets and 2 and 8 on common rectifiers. |
| 2.4 Other components used in amp (a)Potentiometers: These components come in various values and serve different functions. You can think of them as variable resistors. Tone and volume controls are typically potentiometers (pots). Bias supplies also use similar components, but they are different from regular signal or tone pots. |
| (b)Capacitors: These also have different value and voltage ratings in addition to different types of construction. These include polyester film , and electrolytic polarized, ceramic disk, film and foil and Mica type caps. These tend to look very different by design. A polarized cap means it needs to go into the circuit in a particular orientation, usually denoted by a'+' or a '-'on the side of the cap in most cases.Detail about capacitor, please watch Capacitors used in tube guitar amp |
| (c)Resistors: Like capacitors, resistors have different values, types, and voltage ratings. From material consisted, resistors can be divided into carbon comp, metal oxide, metal film, and carbon film serval types. Carbon comps usually look different than carbon film and metal film. Also, generally speaking, the larger the resistor, the greater the power it can tolerate. Common values in tube amps are 220k, 1Meg, 68K, 100K etc. These can be anywhere from 1/2w to 10w, depending on the application. Carbon comps are generally used in Fender amps and Carbon film are used in British style amps historically. |